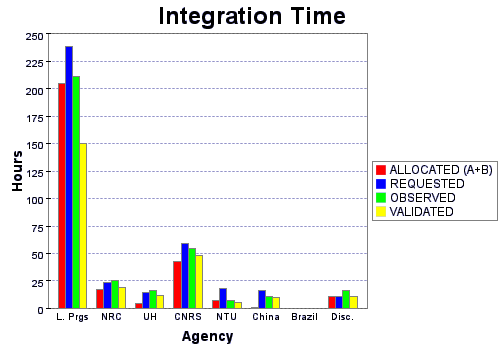

This plot presents the distribution of integration time among the different Agencies. The I-time allocated is the total amount given by the Time Allocation Committees (TAC). The I-time allocated on the telescope is for programs with grades A and B only. The I-time requested is the total amount entered during the Phase 2 and includes also the grade C programs. Due to some programs requesting dynamical intervention with the Phase 2 Tool during a semester, I-time allocated and calculated might sometime differ significantly. The I-time observed is the current total time spent on science targets. The I-time validated corresponds to the current observations validated, that is, considered to be meeting the specifications.
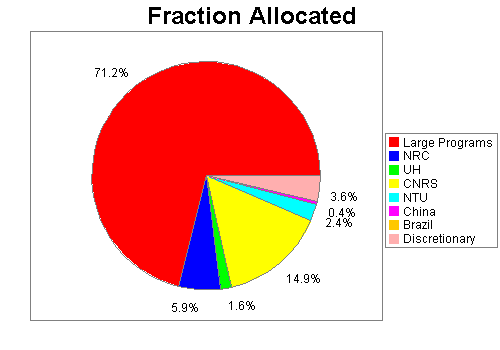
This plot presents the distribution of integration time among the different Agencies, that is, [Total I-time allocated for A and B programs (Agency)]/[Total I-time allocated for A and B programs for all Agencies]. These fractions represent the goal to reach for achieving the correct balance of telescope time for the different Agencies at the end of the semester.

This plot is similar to the previous one but presents the current distribution of the I-time validated among the different Agencies. The goal is to be as close as possible to the fraction requested at the end of the semester. The fraction validated includes A, B and C programs (no snapshots).
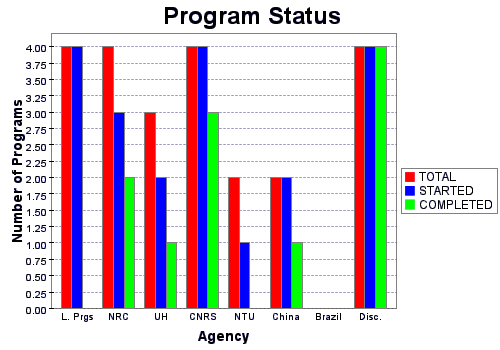
This plot presents the current program status for the semester. Programs completed have all of their observation groups validated.

This plot presents the queue efficiency, that is, the ratio between the number of observations carried out and observations validated. This is a measure of how well we can adapt to sky conditions.